Parrondo's paradox
Parrondo's paradox, a paradox in game theory, has been described as: A losing strategy that wins. It is named after its creator, Spanish physicist Juan Parrondo, who discovered the paradox in 1996. A more explanatory description is:
- Given two games, each with a higher probability of losing than winning, it is possible to construct a winning strategy by playing the games alternately.
Parrondo devised the paradox in connection with his analysis of the Brownian ratchet, a thought experiment about a machine that can purportedly extract energy from random heat motions popularized by physicist Richard Feynman.
Contents |
Illustrative examples
The saw-tooth example
Consider an example in which there are two points A and B having the same altitude, as shown in Figure 1. In the first case, we have a flat profile connecting them. Here, if we leave some round marbles in the middle that move back and forth in a random fashion, they will roll around randomly but towards both ends with an equal probability. Now consider the second case where we have a saw-tooth-like region between them. Here also, the marbles will roll towards either ends with equal probability. Now if we tilt the whole profile towards the right, as shown in Figure 2, it is quite clear that both these cases will become biased towards B.
Now consider the game in which we alternate the two profiles while judiciously choosing the time between alternating from one profile to the other.
When we leave a few marbles on the first profile at point E, they distribute themselves on the plane showing preferential movements towards point B. However, if we apply the second profile when some of the marbles have crossed the point C, but none have crossed point D, we will end up having most marbles back at point E (where we started from initially) but some also in the valley towards point A given sufficient time for the marbles to roll to the valley. Then we again apply the first profile and repeat the steps (points C, D and E now shifted one step to refer to the final valley closest to A). If no marbles cross point C before the first marble crosses point D, we must apply the second profile shortly before the first marble crosses point D, to start over.
It easily follows that eventually we will have marbles at point A, but none at point B. Hence for a problem defined with having marbles at point A being a win and having marbles at point B a loss, we clearly win by playing two losing games.
The coin-tossing example
A second example of Parrondo's paradox is drawn from the field of gambling. Consider playing two games, Game A and Game B with the following rules. For convenience, define 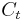 to be our capital at time t, immediately before we play a game.
to be our capital at time t, immediately before we play a game.
- Winning a game earns us $1 and losing requires us to surrender $1. It follows that
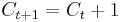 if we win at step t and
if we win at step t and 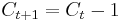 if we lose at step t.
if we lose at step t. - In Game A, we toss a biased coin, Coin 1, with probability of winning
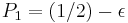 . If
. If 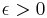 , this is clearly a losing game in the long run.
, this is clearly a losing game in the long run. - In Game B, we first determine if our capital is a multiple of some integer
 . If it is, we toss a biased coin, Coin 2, with probability of winning
. If it is, we toss a biased coin, Coin 2, with probability of winning 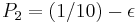 . If it is not, we toss another biased coin, Coin 3, with probability of winning
. If it is not, we toss another biased coin, Coin 3, with probability of winning 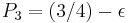 . The role of modulo
. The role of modulo  provides the periodicity as in the ratchet teeth.
provides the periodicity as in the ratchet teeth.
It is clear that by playing Game A, we will almost surely lose in the long run. Harmer and Abbott[1] show via simulation that if 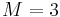 and
and 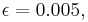 Game B is an almost surely losing game as well. In fact, Game B is a Markov chain, and an analysis of its state transition matrix (again with M=3) shows that the steady state probability of using coin 2 is 0.3836, and that of using coin 3 is 0.6164.[2] As coin 2 is selected nearly 40% of the time, it has a disproportionate influence on the payoff from Game B, and results in it being a losing game.
Game B is an almost surely losing game as well. In fact, Game B is a Markov chain, and an analysis of its state transition matrix (again with M=3) shows that the steady state probability of using coin 2 is 0.3836, and that of using coin 3 is 0.6164.[2] As coin 2 is selected nearly 40% of the time, it has a disproportionate influence on the payoff from Game B, and results in it being a losing game.
However, when these two losing games are played in some alternating sequence - e.g. two games of A followed by two games of B (AABBAABB...), the combination of the two games is, paradoxically, a winning game. Not all alternating sequences of A and B result in winning games. For example, one game of A followed by one game of B (ABABAB...) is a losing game, while one game of A followed by two games of B (ABBABB...) is a winning game. This coin-tossing example has become the canonical illustration of Parrondo's paradox – two games, both losing when played individually, become a winning game when played in a particular alternating sequence. The apparent paradox has been explained using a number of sophisticated approaches, including Markov chains,[3] flashing ratchets,[4] Simulated Annealing[5] and information theory.[6] One way to explain the apparent paradox is as follows:
- While Game B is a losing game under the probability distribution that results for
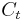 modulo
modulo  when it is played individually (
when it is played individually (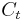 modulo
modulo  is the remainder when
is the remainder when 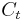 is divided by
is divided by  ), it can be a winning game under other distributions, as there is at least one state in which its expectation is positive.
), it can be a winning game under other distributions, as there is at least one state in which its expectation is positive. - As the distribution of outcomes of Game B depend on the player's capital, the two games cannot be independent. If they were, playing them in any sequence would lose as well.
The role of  now comes into sharp focus. It serves solely to induce a dependence between Games A and B, so that a player is more likely to enter states in which Game B has a positive expectation, allowing it to overcome the losses from Game A. With this understanding, the paradox resolves itself: The individual games are losing only under a distribution that differs from that which is actually encountered when playing the compound game. In summary, Parrondo's paradox is an example of how dependence can wreak havoc with probabilistic computations made under a naive assumption of independence. A more detailed exposition of this point, along with several related examples, can be found in Philips and Feldman.[7]
now comes into sharp focus. It serves solely to induce a dependence between Games A and B, so that a player is more likely to enter states in which Game B has a positive expectation, allowing it to overcome the losses from Game A. With this understanding, the paradox resolves itself: The individual games are losing only under a distribution that differs from that which is actually encountered when playing the compound game. In summary, Parrondo's paradox is an example of how dependence can wreak havoc with probabilistic computations made under a naive assumption of independence. A more detailed exposition of this point, along with several related examples, can be found in Philips and Feldman.[7]
Application of Parrondo's paradox
Parrondo's paradox is used extensively in game theory, and its application in engineering, population dynamics, financial risk, etc., are also being looked into as demonstrated by the reading lists below. Parrondo's games are of little practical use such as for investing in stock markets[8] as the original games require the payoff from at least one of the interacting games to depend on the player's capital. However, the games need not be restricted to their original form and work continues in generalizing the phenomenon. Similarities to volatility pumping and the two-envelope problem[9] have been pointed out. Simple finance textbook models of security returns have been used to prove that individual investments with negative median long-term returns may be easily combined into diversified portfolios with positive median long-term returns.[10] Similarly, a model that is often used to illustrate optimal betting rules has been used to prove that splitting bets between multiple games can turn a negative median long-term return into a positive one. [11]
Name
In the early literature on Parrondo's paradox, it was debated whether the word 'paradox' is an appropriate description given that the Parrondo effect can be understood in mathematical terms. The 'paradoxical' effect can be mathematically explained in terms of a convex linear combination.
However, Derek Abbott, a leading Parrondo's paradox researcher provides the following answer regarding the use of the word 'paradox' in this context:
Is Parrondo's paradox really a "paradox"? This question is sometimes asked by mathematicians, whereas physicists usually don't worry about such things. The first thing to point out is that "Parrondo's paradox" is just a name, just like the "Braess paradox" or "Simpson's paradox." Secondly, as is the case with most of these named paradoxes they are all really apparent paradoxes. People drop the word "apparent" in these cases as it is a mouthful, and it is obvious anyway. So no one claims these are paradoxes in the strict sense. In the wide sense, a paradox is simply something that is counterintuitive. Parrondo's games certainly are counterintuitive—at least until you have intensively studied them for a few months. The truth is we still keep finding new surprising things to delight us, as we research these games. I have had one mathematician complain that the games always were obvious to him and hence we should not use the word "paradox." He is either a genius or never really understood it in the first place. In either case, it is not worth arguing with people like that.
See also
- Ratchet effect
- Brownian ratchet
- Statistical mechanics
- List of paradoxes
- Brazil nut effect
- Game theory
Further reading
- John Allen Paulos, A Mathematician Plays the Stock Market, Basic Books, 2004, ISBN 0-465-05481-1.
- Neil F. Johnson, Paul Jefferies, Pak Ming Hui, Financial Market Complexity, Oxford University Press, 2003, ISBN 0-19-852665-2.
- Ning Zhong and Jiming Liu, Intelligent Agent Technology: Research and Development, World Scientific, 2001, ISBN 981-02-4706-0.
- Elka Korutcheva and Rodolfo Cuerno, Advances in Condensed Matter and Statistical Physics, Nova Publishers, 2004, ISBN 1-59033-899-5.
- Maria Carla Galavotti, Roberto Scazzieri, and Patrick Suppes, Reasoning, Rationality, and Probability, Center for the Study of Language and Information, 2008, ISBN 1-57586-557-2.
- Derek Abbott and Laszlo B. Kish, Unsolved Problems of Noise and Fluctuations, American Institute of Physics, 2000, ISBN 1-56396-826-6.
- Visarath In, Patrick Longhini, and Antonio Palacios, Applications of Nonlinear Dynamics: Model and Design of Complex Systems, Springer, 2009, ISBN 3-540-85631-5.
- Marc Moore, Constance van Eeden, Sorana Froda, and Christian Léger, Mathematical Statistics and Applications: Festschrift for Constance van Eeden, IMS, 2003, ISBN 0-940600-57-9.
- Ehrhard Behrends, Fünf Minuten Mathematik: 100 Beiträge der Mathematik-Kolumne der Zeitung Die Welt, Vieweg+Teubner Verlag, 2006, ISBN 3-8348-0082-1.
- Lutz Schimansky-Geier, Noise in Complex Systems and Stochastic Dynamics, SPIE, 2003, ISBN 0-8194-4974-1.
- Susan Shannon, Artificial Intelligence and Computer Science, Nova Science Publishers, 2005, ISBN 1-59454-411-5.
- Eric W. Weisstein, CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics, CRC Press, 2003, ISBN 1-58488-347-2.
- David Reguera, José M. G. Vilar, and José-Miguel Rubí, Statistical Mechanics of Biocomplexity, Springer, 1999, ISBN 3-540-66245-6.
- Sergey M. Bezrukov, Unsolved Problems of Noise and Fluctuations, Springer, 2003, ISBN 0-7354-0127-6.
- Julián Chela Flores, Tobias C. Owen, and F. Raulin, First Steps in the Origin of Life in the Universe, Springer, 2001, ISBN 1-4020-0077-4.
- Tönu Puu and Irina Sushko, Business Cycle Dynamics: Models and Tools, Springer, 2006, ISBN 3-540-32167-5.
- Andrzej S. Nowak and Krzysztof Szajowski, Advances in Dynamic Games: Applications to Economics, Finance, Optimization, and Stochastic Control, Birkhäuser, 2005, ISBN 0-8176-4362-1.
- Cristel Chandre, Xavier Leoncini, and George M. Zaslavsky, Chaos, Complexity and Transport: Theory and Applications, World Scientific, 2008, ISBN 981-281-879-0.
- Richard A. Epstein, The Theory of Gambling and Statistical Logic (Second edition), Academic Press, 2009, ISBN 0-12-374940-9.
- Clifford A. Pickover, The Math Book, Sterling, 2009, ISBN 1-4027-5796-4.
References
- ^ G. P. Harmer and D. Abbott, "Losing strategies can win by Parrondo's paradox", Nature 402 (1999), 864
- ^ D. Minor, "Parrondo's Paradox - Hope for Losers!", The College Mathematics Journal 34(1) (2003) 15-20
- ^ G. P. Harmer and D. Abbott, "Parrondo's paradox", Statistical Science 14 (1999) 206-213
- ^ G. P. Harmer, D. Abbott, P. G. Taylor, and J. M. R. Parrondo, in Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. Unsolved Problems of Noise and Fluctuations, D. Abbott, and L. B. Kish, eds., American Institute of Physics, 2000
- ^ G. P. Harmer, D. Abbott, and P. G. Taylor, The Paradox of Parrondo's games, Proc. Royal Society of London A 456 (2000), 1-13
- ^ G. P. Harmer, D. Abbott, P. G. Taylor, C. E. M. Pearce and J. M. R. Parrondo, Information entropy and Parrondo's discrete-time ratchet, in Proc. Stochastic and Chaotic Dynamics in the Lakes, Ambleside, U.K., P. V. E. McClintock, ed., American Institute of Physics, 2000
- ^ Thomas K. Philips and Andrew B. Feldman, Parrondo's Paradox is not Paradoxical, Social Science Research Network (SSRN) Working Papers, August 2004
- ^ R. Iyengar and R. Kohli, "Why Parrondo's paradox is irrelevant for utility theory, stock buying, and the emergence of life," Complexity, 9(1), pp. 23-27, 2004
- ^ Winning While Losing: New Strategy Solves'Two-Envelope' Paradox at Physorg.com
- ^ M. Stutzer, The Paradox of Diversification, The Journal of Investing, Vol. 19, No.1, 2010.
- ^ M. Stutzer, "A Simple Parrondo Paradox", Mathematical Scientist, V.35, 2010.
External links
- J. M. R. Parrondo, Parrondo's paradoxical games
- Nature news article on Parrondo's paradox
- Alternate game play ratchets up winnings: It's the law
- Official Parrondo's paradox page
- Parrondo's Paradox - A Simulation
- The Wizard of Odds on Parrondo's Paradox
- Parrondo's Paradox at Wolfram
- Online Parrondo simulator
- Parrondo's paradox at Maplesoft
- Donald Catlin on Parrondo's paradox
- Parrondo's paradox and poker
- Parrondo's paradox and epistemology
- A Parrondo's paradox resource
- Optimal adaptive strategies and Parrondo
- Behrends on Parrondo
- God doesn't shoot craps
- Parrondo's paradox in chemistry
- Parrondo's paradox in genetics
- Parrondo effect in quantum mechanics
- Financial diversification and Parrondo